Table 29
. Atom types--COMPASS (Page 1 of 5)
|
general class
|
atom type
|
description
|
|---|
|
hydrogen types
|
|
h
|
hydrogen, generic
|
|
h1
|
hydrogen, nonpolar
|
|
h1+
|
hydrogen, proton
|
|
h1h
|
hydrogen in H2
|
|
h1n
|
hydrogen bound to N, Cl
|
|
h1o
|
hydrogen bound to O, F
|
|
carbon types
|
|
c
|
carbon, generic
|
|
c1o
|
carbon in carbon monoxide, CO
|
|
c2=
|
carbon, SP, two double bonds O=C=O, S=C=S
|
|
c2t
|
carbon, SP, triple bond
|
|
c3
|
carbon, SP2, generic, 3 bonds
|
|
c3"
|
carbon, SP2, carbonyl, two polar substituents
|
|
c3#
|
carbon, SP2, in CO32- anion
|
|
c3'
|
carbon, SP2, carbonyl, one polar substituent
|
|
c3-
|
carbon, SP2, carboxylate
|
|
c3=
|
carbon, SP2, double bond to C (-C=C-)
|
|
c3a
|
carbon, SP2, aromatic
|
|
c3n
|
carbon, SP2, double bond to N (-C=N-)
|
|
c3o
|
carbon, SP2, carbonyl
|
|
c4
|
carbon, SP3, generic, 4 bonds
|
|
c43
|
carbon, SP3, with 3 heavy atoms
|
|
c44
|
carbon, SP3, with 4 heavy atoms
|
|
c4o
|
carbon, SP3, bond to oxygen
|
|
c4x
|
carbon, SP3, bond to chlorine
|
|
nitrogen types
|
|
n
|
nitrogen, generic
|
|
n1n
|
nitrogen, in N2
|
|
n1o
|
nitrogen in NO
|
|
n1t
|
nitrogen, SP, 1 triple bond
|
|
n2=
|
nitrogen, SP2, 1 double bond, non-aromatic
|
|
n2a
|
nitrogen, SP2, 2 partial double bonds, aromatic
|
|
n2t
|
nitrogen, SP, 1 triple bond, non-aromatic
|
|
n3
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amines
|
|
n3*
|
nitrogen, SP3, in NH3
|
|
n3+
|
nitrogen, SP3, charged
|
|
n3a
|
nitrogen, SP2, aromatic
|
|
n3h1
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amines with 1 hydrogen
|
|
n3h2
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amines with 2 hydrogens
|
|
n3m
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amides without hydrogen
|
|
n3mh
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amides with hydrogen
|
|
n3o
|
nitrogen, SP2, in nitro group
|
|
n4+
|
nitrogen, SP3, in protonated amine
|
|
n4o
|
nitrogen, SP3, in amine oxide
|
|
oxygen types
|
|
o
|
oxygen, generic
|
|
o-2
|
oxygen, anion in metal oxides (O-2)
|
|
o1-
|
oxygen, SP2, in carboxylate
|
|
o12
|
oxygen, SP2, in nitro group (-NO2)
|
|
o1=
|
oxygen, SP2, in carbonyl
|
|
o1=*
|
oxygen, in CO2
|
|
o1c
|
oxygen, in CO
|
|
o1n
|
oxygen, in NO
|
|
o1o
|
oxygen, in O2
|
|
o2
|
oxygen, SP3, generic
|
|
o2*
|
oxygen, SP3, in water
|
|
o2a
|
oxygen, SP2, aromatic, in 5-membered ring
|
|
o2b
|
oxygen, SP3, bridge atom in anhydrides
|
|
o2c
|
oxygen, SP3, in acids
|
|
o2e
|
oxygen, SP3, in ethers
|
|
o2h
|
oxygen, SP3, in alcohol
|
|
o2s
|
oxygen, SP3, in esters
|
|
o2z
|
oxygen, in siloxanes and zeolites
|
|
o3
|
oxygen, in H3O+
|
|
o3z
|
oxygen, bridge in zeolites
|
|
sulfur types
|
|
s
|
sulfur, generic
|
|
s1=
|
sulfur, 1 double bond (=S)
|
|
s2
|
sulfur, 2 single bonds (-S-)
|
|
s2=
|
sulfur, 2 double bonds (=S=)
|
|
s2a
|
sulfur, in aromatic ring (thiophene)
|
|
s3=
|
sulfur, 3 bonds, 1 is double
|
|
s4
|
sulfur, 4 single bonds
|
|
s4=
|
sulfur, 4 bonds, 2 are double
|
|
s6
|
sulfur, 6 single bonds
|
|
phosphorus types
|
|
p
|
phosphorus, generic
|
|
p4=
|
phosphorus, in phosphazenes
|
|
halogen types
|
|
br
|
bromine, generic
|
|
br-
|
bromine, anion
|
|
br1
|
bromine, one bond
|
|
cl
|
chlorine, generic
|
|
cl-
|
chlorine anion
|
|
cl1
|
chlorine, one bond
|
|
cl12
|
chlorine, to a carbon that has 2 X
|
|
cl13
|
chlorine, to a carbon that has 3 X
|
|
cl14
|
chlorine, to a carbon that has 4 X
|
|
cl1p
|
chlorine, in phosphazenes
|
|
f
|
fluorine, generic
|
|
f-
|
fluorine anion
|
|
f1
|
fluorine, one bond
|
|
f12
|
fluorine, to a carbon that has 2 F
|
|
f13
|
fluorine, to a carbon that has 3 F
|
|
f14
|
fluorine, to a carbon that has 4 F
|
|
f1p
|
fluorine, in phosphazene
|
|
i
|
iodine, generic
|
|
i-
|
iodine anion
|
|
i1
|
iodine, with one bond
|
|
metal types
|
|
Ag
|
silver, metal
|
|
Al
|
aluminum, metal
|
|
Au
|
gold, metal
|
|
Cr
|
chromium, metal
|
|
Cu
|
copper, metal
|
|
Fe
|
iron, metal
|
|
Mo
|
molybdenum, metal
|
|
Ni
|
nickel, metal
|
|
Pb
|
lead, metal
|
|
Pd
|
palladium, metal
|
|
Pt
|
platinum, metal
|
|
Sn
|
tin, metal
|
|
W
|
tungsten, metal
|
|
metal ion types
|
|
ca+
|
calcium ion (Ca2+)
|
|
cu+2
|
copper ion (Cu2+)
|
|
fe+2
|
iron ion (Fe2+)
|
|
mg+2
|
magnesium ion (Mg2+)
|
|
zn+2
|
zinc ion (Zn2+)
|
|
alkali metal and ion types
|
|
K
|
potassium, metal
|
|
Li
|
lithium, metal
|
|
Na
|
sodium, metal
|
|
cs+
|
cesium ion (Cs+)
|
|
k+
|
potassium ion (K+)
|
|
li+
|
lithium ion (Li+)
|
|
na+
|
sodium ion (Na+)
|
|
rb+
|
rubidium ion (Rb+)
|
|
zeolite and silicon types
|
|
al4z
|
aluminum, in zeolites
|
|
si
|
silicon, generic
|
|
si4
|
silicon, generic with 4 bonds
|
|
si4c
|
silicon, in siloxane with heavy atoms only
|
|
si4z
|
silicon, in zeolites
|
|
noble gas types
|
|
ar
|
argon
|
|
he
|
helium
|
|
kr
|
krypton
|
|
ne
|
neon
|
|
xe
|
xenon
|


![]()

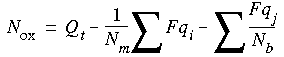 where Qt is the total charge on the complex, and the sums over Fqi and Fqj are the sums of formal charges on atoms not bonded to metals and bonded to metals, respectively. Nm is the number of metal atoms in the complex, and Nb is the number of metal atoms bonded to the jth ligand atom.
where Qt is the total charge on the complex, and the sums over Fqi and Fqj are the sums of formal charges on atoms not bonded to metals and bonded to metals, respectively. Nm is the number of metal atoms in the complex, and Nb is the number of metal atoms bonded to the jth ligand atom.![]()
